Bard is Google’s public entry into the highly competitive field of artificial intelligence chatbots, which also includes OpenAPI’s ChatGPT. Google intends Bard to be a “creative and helpful collaborator” that people may chat with using natural language. The following guide covers what you need to know as you chat and explore the capabilities of Google Bard.
Jump to:
- What is Google Bard?
- What is Google Bard used for?
- Can I use Google Bard for work or school?
- How to get access to Google Bard
- How to use Google Bard
- Frequently asked questions about Google Bard
What is Google Bard?
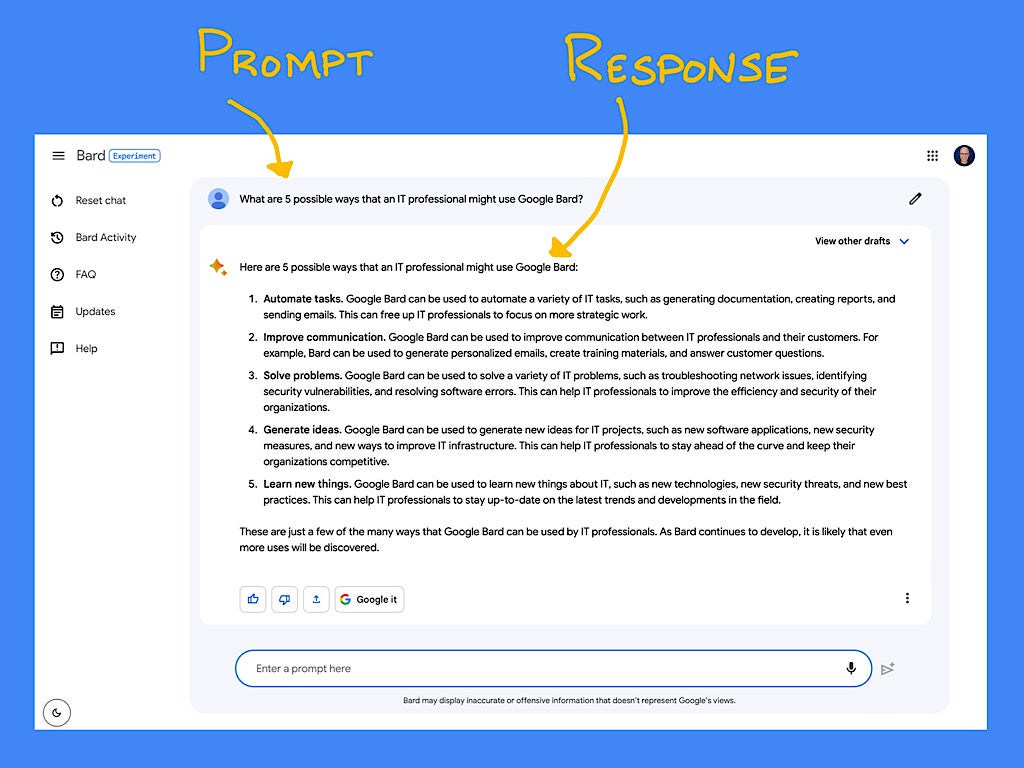
Google Bard is an AI chatbot: After you enter a text prompt, Bard generates a response. Importantly, Bard can access the internet to leverage Google search for its responses.
Google launched Bard in early 2023 as an experiment that is based on a conversational large language model.
What is Google Bard used for?
Bard can serve as an AI collaborator to help you explore topics, craft text and code. Anything you might ask a knowledgeable colleague or friend might be a candidate for a prompt in Bard. For example, you could use Bard to:
- Discover options or brainstorm ideas.
- Explore a topic or identify related items, books or concepts.
- Draft an email.
- Create an outline for a blog post, project, proposal or book.
- Simplify, rephrase or summarize text.
- Help create or debug code.
Bard can also streamline a search. For example, consider the task of gathering specifications to select a laptop. With a conventional Google Search, you would search for a product, follow a link, then copy details into a Google Doc. Then you would repeat the process for each additional laptop you wished to compare. With Bard, you could enter a single prompt that asks the system to compare two, three or more laptops and present the information in a table format, then export the response to a Google Doc. What used to be several steps may be reduced to two: Prompt, then export.
Can I use Google Bard for work or school?
Yes, you may use Google Bard for work or school if your organization’s policies and Google Workspace settings allow it.
How to get access to Google Bard
You may use Bard in any modern browser, such as Chrome, Safari, Edge or Firefox; however, you will need to sign in with a Google account to gain access, as follows.
- Go to bard.google.com in a browser.
- Select Sign In (Figure A).
Figure A

- Sign in with your Google account.
- Select Try Bard (Figure B).
Figure B

- Review the presented terms (Figure C) and, if you agree, accept them.
Figure C

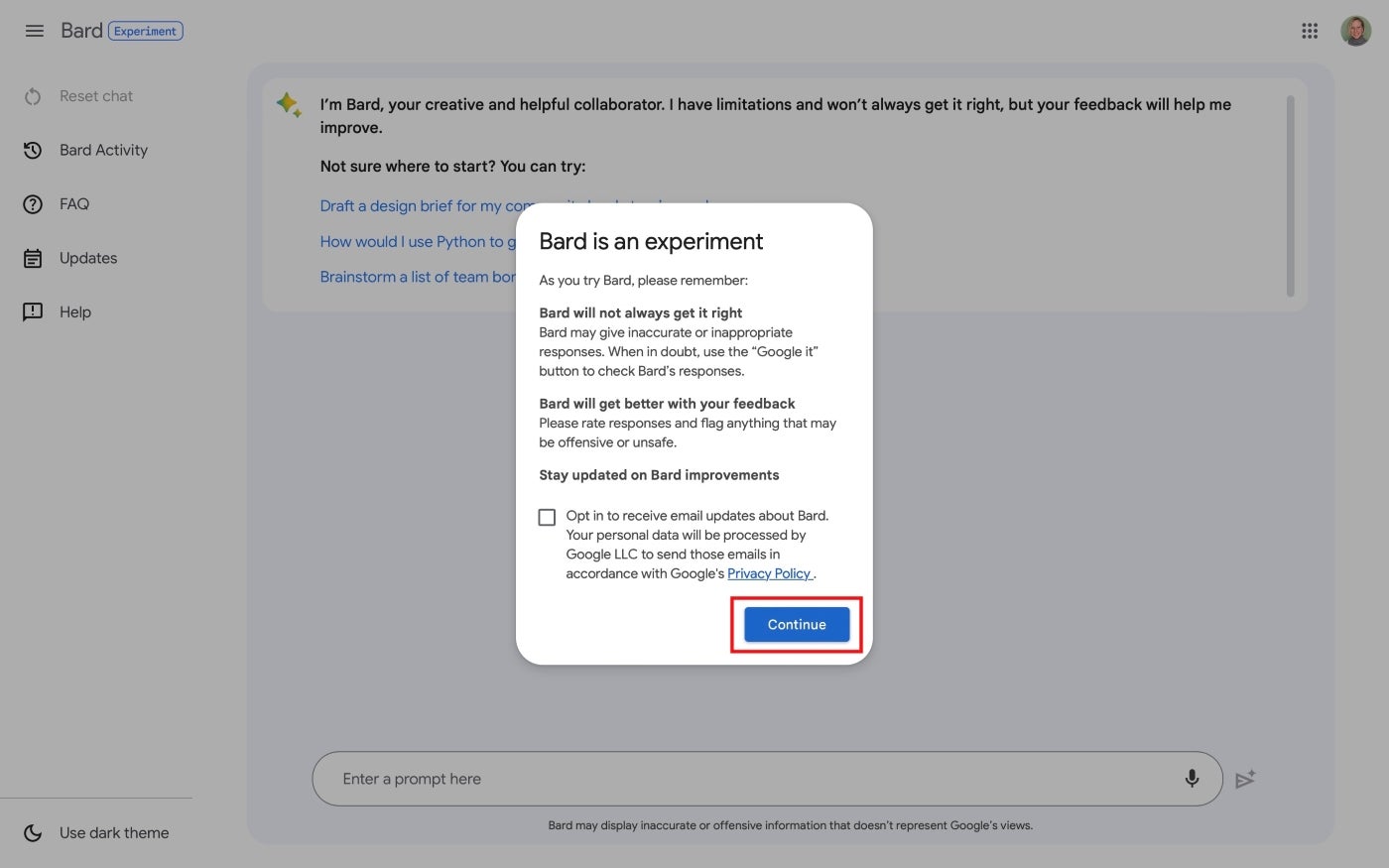
- Review the “Bard Is An Experiment” note and, if you wish, opt in to receive email updates about Bard, then select Continue (Figure D).
Figure D
- Use Bard by entering a prompt in the box near the bottom of the screen (Figure E).
Figure E

For the easiest access to Bard, you might consider adding Bard as a bookmark or set the site as your browser homepage. Since Bard works in a variety of browsers, fast-access techniques work not only from Chrome, but also from other systems. For example, in Safari on an iPhone from bard.google.com you could select the Share button | Add To Home Screen to place a Bard app link on your phone.
How to use Google Bard
You may access Bard from any mobile or desktop web browser while signed in to a Google account.
- Open bard.google.com in a browser.
- Enter a prompt, either by typing or selecting the microphone and talking. Press enter (or return) to send the prompt to Bard.
- Review Bard’s response.
Once Bard provides a response, the system offers a robust set of optional actions (Figure F).
Figure F

You may:
- Edit the prompt text to try a variant prompt.
- View other drafts to evaluate differently structured responses.
- Regenerate drafts to seek alternative responses.
- “Google it” to switch to a standard keyword search query derived from your prompt.
- Export the response to a new Gmail or a Google Doc.
- Copy the content to paste into another app.
- Report a legal issue to signal a significant content concern.
- Provide feedback with a thumbs up (Good Response) or down (Bad Response) button.
- Enter another prompt to continue the chat.
Frequently asked questions about Google Bard
How accurate is Google Bard?
As an experiment, Google tries to ensure that Bard responses are accurate, but prominently cautions that “Bard may display inaccurate or offensive information that doesn’t represent Google’s views.” When you use Bard, you should verify the accuracy of any response provided.
How does Google Bard compare to a Google Search?
Google Search provides relevant links in response to keywords. When the system is highly certain that a specific answer is relevant, Google Search may prominently feature the desired information, such as a snippet of content from Wikipedia, a sports score or weather data.
Google Bard provides responses to natural language prompts. Unlike search, where each keyword query returns an answer and list of links, a Bard response may be just the start of a string of interactions in a chat-like format. At any point, you may prompt Bard to expand, clarify, rephrase or regenerate a response.
How does Google Bard compare to ChatGPT?
ChatGPT is a large language model system from OpenAI that offers both free and paid editions. OpenAI and Microsoft have announced a wide range of product integrations and partnerships, including connections between ChatGPT and Microsoft Bing. GPT-4 provided significant performance improvements over earlier editions.
Bard is a large language model system experiment from Google that is free for people to use. Bard relies on current internet information via Google Search.
Google, Microsoft and OpenAI are iterating rapidly to enhance and expand the capabilities of their respective AI systems.
What are the main competitors to Google Bard?
In addition to ChatGPT, alternatives to Google Bard include Microsoft’s new Bing, Perplexity AI, Inflection AI’s Pi and Anthropic’s Claude, which is available via Quora’s Poe AI chat app.
Can Google Bard search the internet?
Yes, since Bard has access to Google Search content, the system may access web news, information and other content.
Does Google Bard keep my data?
Google lets you adjust settings to control whether Bard Activity is preserved. To preserve all your Bard Activity history, turn Bard Activity on and set auto-delete off. Alternatively, you may choose to auto-delete Bard activity older than 3, 18 or 36 months.
If you prefer, you may turn Bard Activity history off. Even when Bard Activity history is off, though, the system will preserve conversations for up to 48 hours, although any activity won’t display in your activity history. According to Google, this temporary retention “allows us to provide the service and process any feedback.”